XL CBFB/MYH11 plus
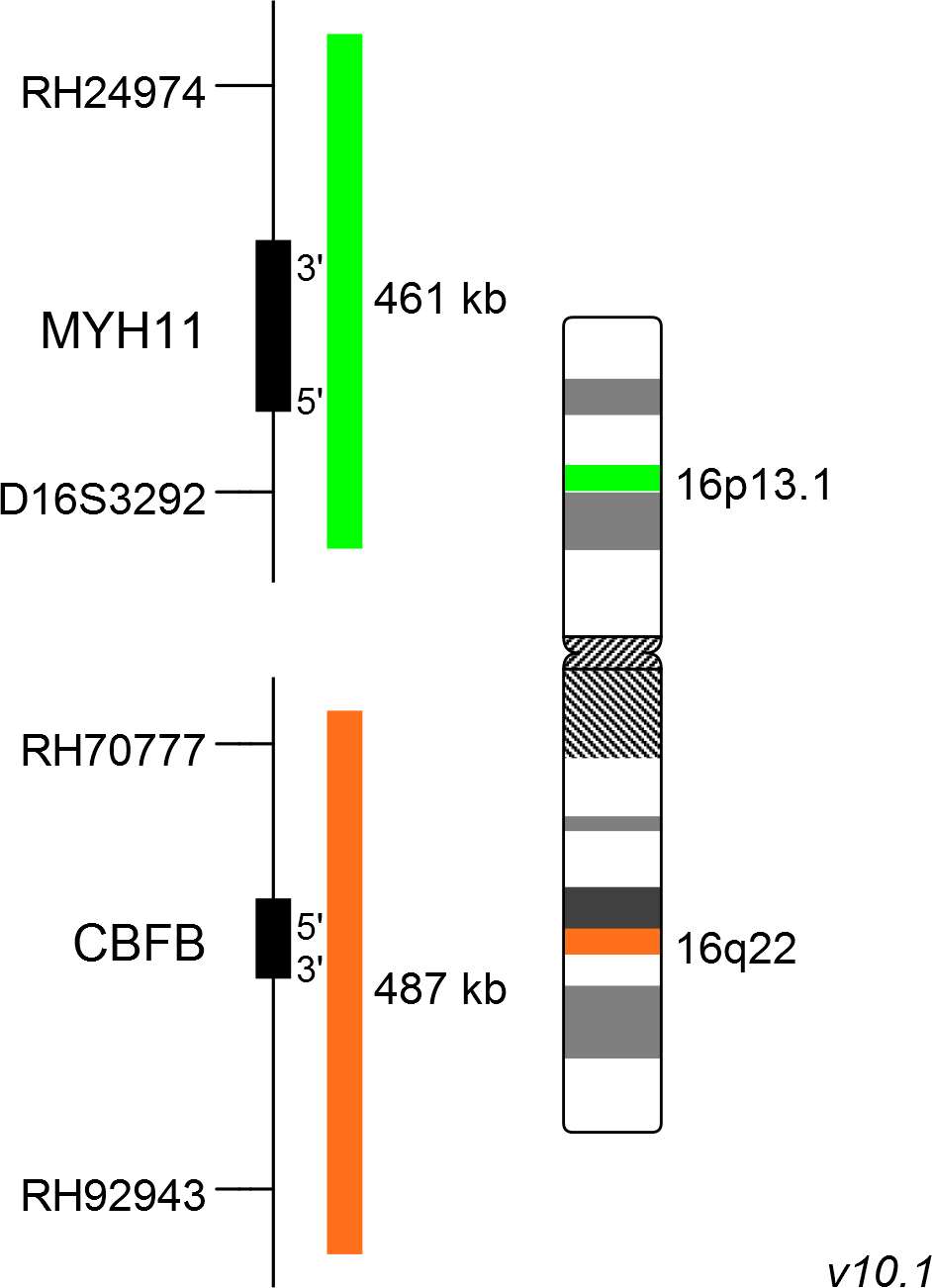
XL CBFB/MYH11 plus is designed as a dual fusion probe. The orange labeled probe spans the breakpoint at 16q22 (CBFB), and the green labeled probe spans the breakpoint at 16p13 (MYH11).
Acute myeloid leukemia with inv(16)(p13.1;q22) and t(16;16)(p13.1;q22) is listed in the World Health Organization classification of tumors of the haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. These recurrent rearrangements are present in about 10% of young AML patients. In cases with inv(16)/t(16;16), the core binding factor b (CBFB) gene on 16q22 is fused with the smooth muscle myosin heavy chain gene (MYH11) on 16p13.1. Patients carrying inv(16)/t(16;16) usually have a good prognosis. Cryptic insertions with no indication in cytogenetic analyses have been published. In these cases, a partial insertion of MYH11 into CBFB, or a partial insertion of CBFB into the MYH11 gene was observed. FISH probes with a break-apart design might overlook this cryptic rearrangement because no separation of flanking regions of CBFB occurs whereas translocation/dual fusion FISH probes are indicating this kind of cryptic rearrangement. FISH is a complementary method for the detection of inv(16)/t(16;16) increasing the sensitivity in combination with conventional cytogenetics. Furthermore, FISH is a valuable tool for cases without assessable metaphases.
Cena za kus: pro registrované
Acute myeloid leukemia with inv(16)(p13.1;q22) and t(16;16)(p13.1;q22) is listed in the World Health Organization classification of tumors of the haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. These recurrent rearrangements are present in about 10% of young AML patients. In cases with inv(16)/t(16;16), the core binding factor b (CBFB) gene on 16q22 is fused with the smooth muscle myosin heavy chain gene (MYH11) on 16p13.1. Patients carrying inv(16)/t(16;16) usually have a good prognosis. Cryptic insertions with no indication in cytogenetic analyses have been published. In these cases, a partial insertion of MYH11 into CBFB, or a partial insertion of CBFB into the MYH11 gene was observed. FISH probes with a break-apart design might overlook this cryptic rearrangement because no separation of flanking regions of CBFB occurs whereas translocation/dual fusion FISH probes are indicating this kind of cryptic rearrangement. FISH is a complementary method for the detection of inv(16)/t(16;16) increasing the sensitivity in combination with conventional cytogenetics. Furthermore, FISH is a valuable tool for cases without assessable metaphases.
Cena za kus: pro registrované




